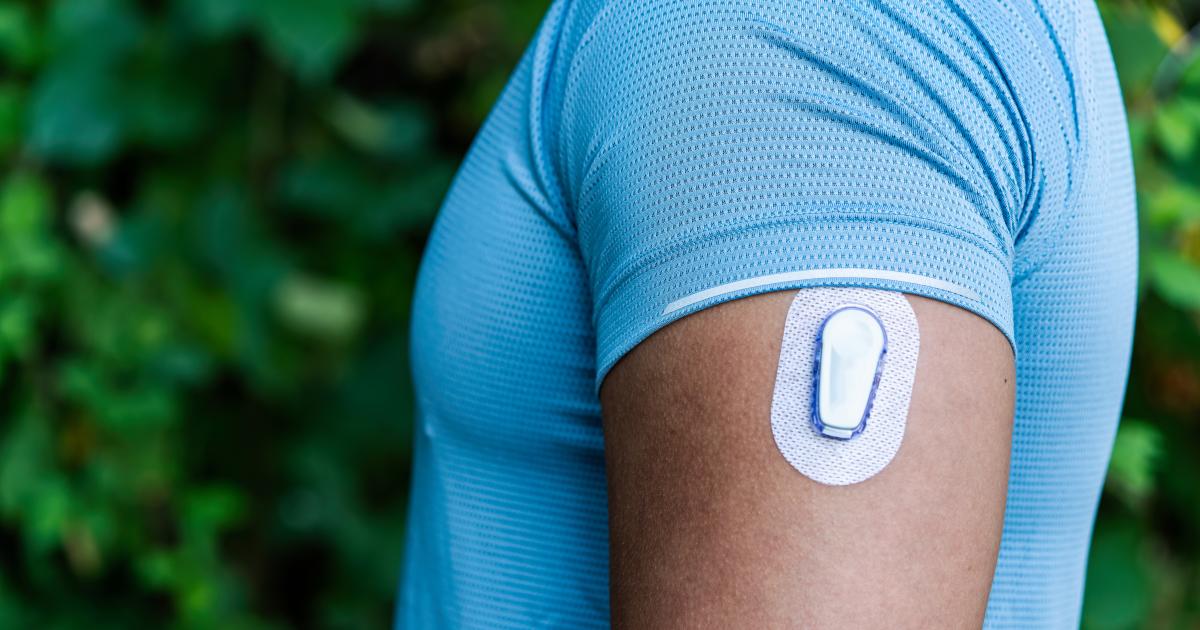
“Let’s see what a Snickers bar does to my blood sugar,” Justin Richard, a 52-year-old Toronto-based TikToker says just before eating the candy bar on camera. After an edited time skip, Richard says, “It’s been several hours since I’ve had the chocolate bar, let’s have a look at the glucose monitor and see what actually happened.” He slightly lifts his arm flashing the device, an inconspicuous blue circular patch that almost looks like a Band-Aid. Above his head flashes a screenshot of his blood glucose reading, which appears to have spiked, dipped, and spiked again. “I had a spike in my blood sugar,” he says. “That’s not a shock because this is loaded with sugar.” A red ‘X’ graphic appears over some b-roll of the Snickers bar. “I did this test because I’m trying to establish a benchmark.”
This is a typical 60-second TikTok from Richard, whose handle is @insulinresistant1 on the platform. In the following clip, Richard eats a cup of broccoli before eating another full Snickers bar, then goes on to share the results of his blood glucose levels from his personal continuous glucose monitor. He eats this oddball combination to show how variations in his food intake can impact or even prevent a blood glucose spike.
Continuous glucose monitors (or CGMs) have long been used as a tool to track blood sugar levels for people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Here’s the thing, though: Richard does not have diabetes.
While monitoring sugar intake is standard practice for people on tight blood sugar control treatment plans and those with persistently low blood glucose levels, modern CGM devices – non-invasive wearables that can attach to the back of an arm for weeks at a time – have become a popular wellness trend on social media. Users like Richard that have integrated a CGM into their daily life have stormed platforms like TikTok and Instagram. Some internet health coaches and dieticians have trumpeted their praise. On TikTok, the hashtags #insulinresistance has 1.2 billion views, while #continuousglucosemonitor has over 32.7 million views. Richard, who has over 800,000 TikTok followers, is just one influencer who helped fuel this trend. On his page, which he started during the pandemic, showcases him eating a wide range of foods and drinks, from sodas to chocolate bars, reacting to readings emitting from his Signos-sponsored CGM device.
Richard says he got into continuous glucose monitoring to “optimize his health” and prevent chronic illness, which was especially important to him considering his extensive family history of Type 2 diabetes. “It’s like having a coach,” he said in an interview. “But the coach is telling you to do something.” That something was to make some pretty dramatic dietary changes. “’I’m not a healthcare professional and I don’t pretend to be. All of my tests are about my blood sugar, and what I read online and how it affects me,” he said, adding that his disclaimer that “individual results will vary” is a key part of his messaging.
Getty Images
Blood glucose monitoring devices are not new. In the late 1990s, medical companies like Medtronic, Dexcom and Abbott revolutionized the way diabetes could be managed. The importance of continuous glucose monitoring for patients is well established as a means of improving glycemic control, especially in the case of Type 1 diabetes.
CGMs are a vital tool for preventing diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening complication seen in Type 1 diabetic patients. When sugar levels are too high and the body begins to break down fat as fuel, it can lead to a high amount of acid circulation in the bloodstream. For non-diabetics, however, complications stemming from extremely high or low blood sugar levels isn’t a concern. There is little to no research to back that monitoring blood glucose levels in generally healthy adults equates to an overall improvement in health.


Getty Images
Dr. Idz, another TikToker with over 1.7 million followers, calls the use of CGM devices for adults without any prescribed medical need a “feature of disordered eating.” Dr. Idz, short for Idrees Mughal, is a board-certified UK-trained medical doctor with expertise in nutritional research. He became a prominent figure when he started rebuking the “nonsense health information” circulating on TikTok that “prey[s] on people’s vulnerabilities.” He says CGMs aren’t really intended for non-diabetics because “our body is designed to regulate the spike.” Dr. Idz says people need to understand that spiking blood glucose is not a problem. In fact, that is supposed to happen when you eat food. Even eating protein can spike your insulin levels. This is important because people are scared of blood glucose spikes because it “spikes your insulin” and they think that causes fat gain and insulin resistance, Dr. Idz explains. “But no one really hypes on about that, right?”
Although there may not be an inherent physical risk for people who wear a CGM device to monitor and track sugar levels, there is a real possibility that access to “too much data” can lead to information overload, false alarms, unnecessary anxiety, confusion or misinterpretation. Slight fluctuations in blood sugar levels are normal in people who don’t have diabetes. Dr. Robert Shmerling, a senior faculty editor for Harvard Health Publishing and author of “Is blood sugar monitoring without diabetes worthwhile?” writes that, “we’re at the very beginning of the learning curve for home monitoring of blood sugar in people without diabetes. Before buying into what may be the next fad in health monitoring, I think we need to learn a lot more.”
Still, it’s no surprise that more people are interested in experimenting with CGM devices. Not only are TikTokers promoting blood glucose monitoring as an indicator of health and wellness, but ads for CGM devices from up-and-coming brands like Nutrisense, Veri and Signos have been flooding social media.
The companies use language designed to sell the average person on the importance of regularly tracking blood sugar levels as a way to lose weight or as a “metabolism hack.” The idea is that eating refined carbs and sugary foods can spike blood glucose levels and, over time, the cells that are supposed to take up insulin and regulate glucose production in the liver become resistant to the hormone due to habitual bad dieting. Heather Davis, a registered and licensed dietitian and nutritionist at Nutrisense denies that the company promises weight loss through glucose monitoring. “A CGM is not a weight loss device per se,” she said. “The CGM is simply one tool among many that may support insights into how different dietary and lifestyle approaches influence metabolic health, including weight factors.”


Getty Images/iStockphoto
Dr. Idz would disagree with Nutrisense on that. He argues that the vast majority of people won’t even know how to interpret CGM results. “Even me as a medical doctor, I would probably need to look at some reference values for each individual, you know, perhaps have to do some calculations. And that’s me who’s actually a medical doctor. Imagine the average person who’s just going, ‘oh, my gosh, I’ve had a spike. That must mean it’s bad, right?’ You don’t even know how to interpret it. So it’s going to be completely useless.”
Nutrisense’s Davis concedes that there is limited research currently looking at CGM use in non-diabetic populations, but she argues that “once upon a time, there was also limited research looking at CGM use in diabetic populations” and that the “risks of wearing a CGM are extremely minimal for most people.” Still, the FDA has never recommended continuous glucose monitoring for healthy individuals. It has only even approved a handful of devices for people who do suffer from diabetes. Although it may be useful for predicting a risk for pre-diabetes and diabetes, there is a consensus that more scientific studies are needed to observe CGM use among healthy populations.
Companies marketing their wearables to healthy people are entering a crowded, but growing market that’s ripe for exploitation. There is arguably an enormous opportunity for companies advertising to healthy individuals to reap financial benefits from the latest health fad.

Signos
TikToker Richard says he thinks continuous glucose monitoring is only going to grow from here. “I don’t think this trend is going to end anytime soon,” he said. “Anybody and every country that’s adopted this fast food, highly processed diet is having this same increase in Type 2 diabetes and you really can’t ignore it. So I think this trend is gonna continue as long as this fast food is so prevalent.” Dr. Idz, on the other hand, would argue that if you want to prevent diabetes, “that’s fine but you’re not going to do it by wearing a CGM because you know, as long as you’re not insulin resistant, you’ll find that you don’t need a CGM.”
To make matters worse, not only are CGMs questionably useful for healthy individuals, but they can be expensive, too. The devices must be replaced every seven to 14 days depending on the manufacturer. Nutrisense does not accept insurance coverage on the grounds it is a “wellness program,” with monthly subscriptions starting at $225 and no-commitment plans reaching $399 a month. Competitors like Signos, which accepts insurance with a diabetes diagnosis, offers a monthly plan for its wearable and monitoring app, and that costs upwards of $449 a month. Veri may accept insurance, depending on the provider. And even though it’s able to dramatically undercut its competitors, the monthly fee of between $40 to $109 is hardly cheap. Richard, who has historically paid out of pocket for his CGM devices, believes the high cost is going to “save him money in the long run.”
Unfortunately, these lofty prices don’t just affect health-conscious TikTokers. Access to CGM devices for diabetic populations can be spotty. Individuals covered by Medicaid are less likely to have one covered, especially people of color, according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA).
Aside from the technology’s often inaccessible price points, some experts argue that there simply isn’t enough guidance from the scientific community on CGM applications for healthy individuals. The ADA does not recommend CGM device use by healthy people, only clearly stating that the technology should be considered “from the outset of the diagnosis of diabetes that requires insulin management.”
Dr. Idz takes this a step further, stating flatly that “there is no evidence whatsoever that blunting blood sugar spikes does anything for our health.” He backs up his argument with research from a retrospective and randomized trial that focused on the impact of blood glucose monitoring in diabetic and non-diabetic populations. Dr. Idz says, if anything, research suggests that a low average blood glucose level is bad for you and might increase mortality risk over time due to diminished consumption of healthy nutrients and decreased liver function.
Harvard’s Dr. Shmerling reports he could not find a published study suggesting that monitoring blood glucose levels directly translated into improved health. “Unfortunately, some makers of CGM systems aren’t waiting for solid research results to market these devices to healthy people. So, consumers and marketing professionals — not researchers or doctors — may wind up driving demand for the product,” Dr. Shmerling writes. Despite the lacking body of evidence to support blood glucose monitoring among healthy populations, the inflated price points for direct to consumer products, and the technological handicaps still present in the burgeoning industry, the growing popularity of CGMs among health and fitness enthusiasts does not seem to be slowing down.
Update, July 18th 2023, 2:17 PM ET: This story has been updated to clarify that Dr. Idz had mistakenly said glucose when he meant insulin.
This story originally appeared on Engadget